Arduino Architecture
The firmware is split into two cooperating sketches:
- Sensor Node:
Arduino/ESP-Node/ESP-Node.ino - Gateway:
Arduino/ESP-Gateway/ESP-Gateway.ino
The flow-level view is captured in the diagrams below, while the rest of this page documents the concrete behavior that appears in the code.
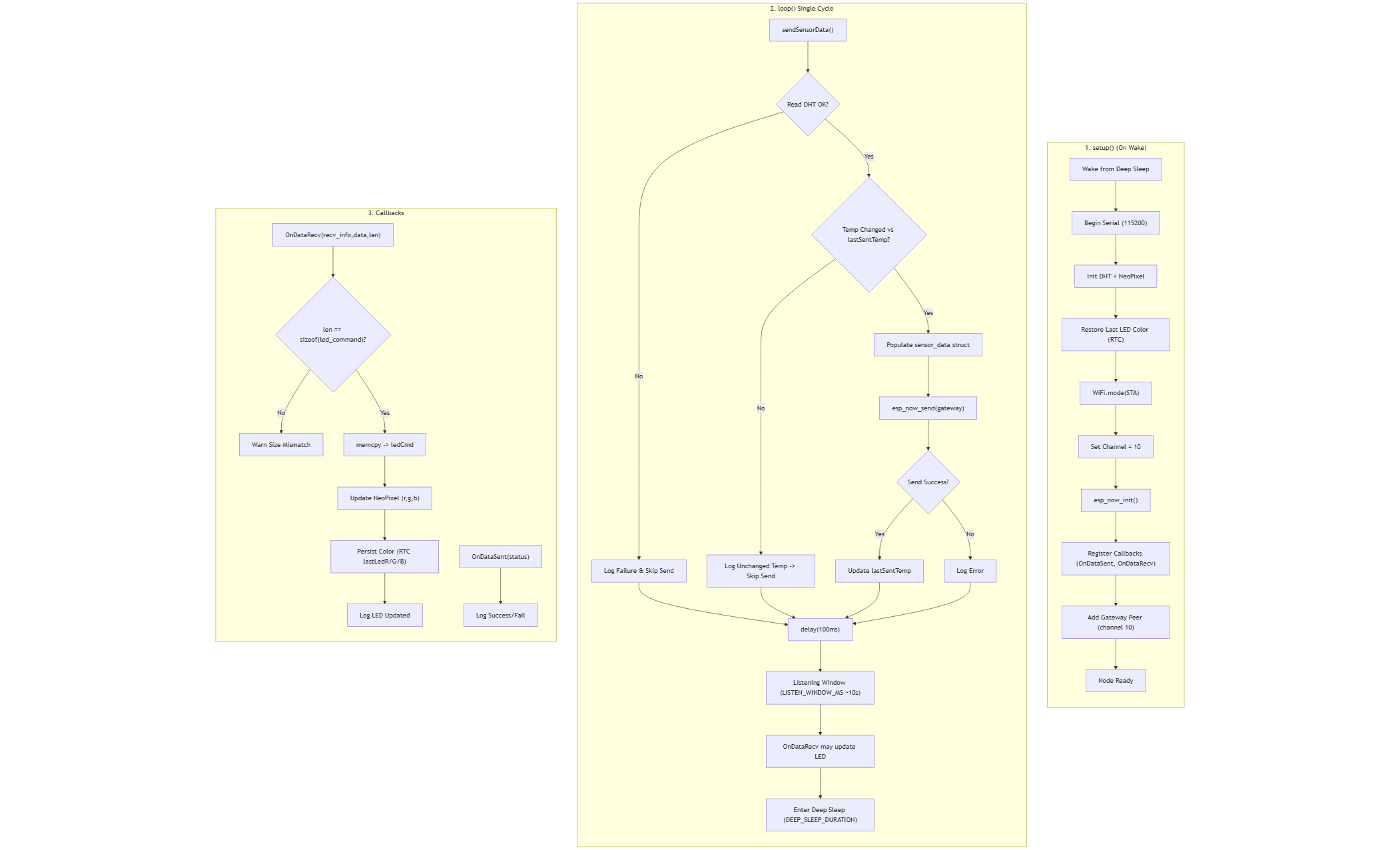
Sensor Node Firmware (ESP-Node.ino)
Hardware and libraries
- ESP32 running in STA mode with ESP-NOW enabled on WiFi channel 10.
- DHT11 sensor on pin
DHT_PIN = 4via theDHTlibrary. - Single NeoPixel on
RGB_PIN = 5driven byAdafruit_NeoPixel.
Power and timing strategy
- Deep sleep for 10 seconds (
DEEP_SLEEP_DURATION = 10,000,000microseconds) between wake cycles. - On wake: initialize peripherals, restore the last LED color from RTC memory, and re-register the gateway peer on channel 10.
- After transmitting data, the node keeps ESP-NOW active for a 10-second listening window (
LISTEN_WINDOW_MS = 10000) so it can receive LED updates before returning to deep sleep.
Sensor publishing flow
- Read temperature and humidity from the DHT11.
- Skip transmission if the temperature has not changed since the previous send (
lastSentTemp). - Populate the packed struct:
int nodeIDfloat tempfloat hum
- Send via
esp_now_sendto the hard-coded gateway MAC0xF0F5BDFB26B4. - Update
lastSentTemponly on successful send.
LED handling
- LED commands reuse a packed struct (
turnOn,r,g,b). - The node prints the sender MAC, validates the payload size, and immediately updates the NeoPixel color.
- Latest LED color is persisted in RTC memory (
lastLedR/G/B) and restored on the next wake so the LED state survives deep sleep.
Gateway Firmware (ESP-Gateway.ino)
Connectivity and peers
- Connects to WiFi SSID
B31IOT-MQTT(station mode). ESP-NOW is initialized afterward so it shares the WiFi channel. - Registers up to four ESP-NOW peers (MACs listed in the sketch) corresponding to each sensor node.
- MQTT broker:
broker.hivemq.comusing thePubSubClientlibrary.
MQTT topics
- Publish telemetry:
EnvPublish4482 - Threshold updates (subscribe):
ThreshCheck4482 - LED override control (subscribe):
LEDOverride4482 - Testing/diagnostics publish:
TestTopic4482
Data handling pipeline
OnDataRecvcopies the packedsensor_datastruct and records temperature, humidity, last update timestamp, and active state per node.- Every 5 seconds (
publishInterval = 5000),publishToNodeRED()emits a JSON payload of the form{ "d": { node1_temp, node1_hum, ... }, "alarm": bool, "threshold": value }onEnvPublish4482when MQTT is connected. - Threshold updates arrive as JSON on
ThreshCheck4482and directly adjustTEMP_THRESHOLD. checkTemperatureThreshold()setsalarmActiveif any active node exceeds the current threshold within the last 30 seconds.
LED strategy
- Remote override: JSON payload on
LEDOverride4482togglesremoteOverrideActiveand supplies RGB values that are broadcast immediately. - Default behavior: even without an override, the gateway stores the last LED command (
overrideOn/R/G/B) and pushes it to the responding node whenever data is received. - Periodic broadcast: every 3 seconds (
ledBroadcastInterval = 3000) the gateway callsbroadcastLEDCommand()so sleeping nodes that wake between transmissions still receive the latest LED state.
Reliability aspects
- MQTT connection watchdog attempts to reconnect every 5 seconds when disconnected.
- ESP-NOW callbacks log send failures to help troubleshoot peer registrations.
- WiFi channel alignment is logged so mismatches between node channel 10 and the access point channel can be addressed quickly.
Data and LED Flow Summary
- Nodes wake, sample, and send only when the temperature changes, minimizing airtime and energy use.
- Gateway ingests ESP-NOW frames, mirrors LED status back to the sender, and updates MQTT clients with the aggregated view.
- Node-RED consumes
EnvPublish4482, displays dashboards, and can publish threshold or LED override commands that immediately influence gateway logic. - LED commands remain synchronized due to the periodic gateway broadcast and the node’s 10-second listening window after each send.
These behaviors correspond to the flowcharts above and the detailed Node-RED accompaniment documented in docs/node_arch.md.